PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION

Chapter at a glance:
Here are detailed notes on Professional Communication suitable for a BTech 1st year course. These notes cover essential aspects of communication within a professional context, focusing on skills and practices that are vital in a technical or business environment.
1. Introduction to Communication
Communication is the process of sharing or exchanging information, ideas, and feelings between individuals or groups. It can take various forms such as verbal, non-verbal, and written. Effective communication is key to building relationships and ensuring understanding.
2. Importance of Professional Communication
In a professional setting, communication is crucial for:
- Team Collaboration: Helps in coordinating tasks, sharing information, and working toward common goals.
- Problem-Solving: Clear communication assists in identifying problems and finding solutions.
- Leadership and Management: Leaders use communication to guide, motivate, and organize teams.
- Career Success: Strong communication skills enhance your professional image, build networks, and help you move up in your career.
3. Characteristics of Professional Communication
- Clarity: The message should be clear and easy to understand, avoiding ambiguity.
- Conciseness: Keep messages brief and to the point, while still conveying all necessary information.
- Courtesy: Politeness and respect are essential in professional communication.
- Formality: Professional communication often requires a formal tone, especially in written documents and official meetings.
- Accuracy: Facts and information shared must be precise to avoid misunderstandings.
4. Types of Professional Communication
a. Verbal Communication
This includes spoken communication through direct conversation, presentations, phone calls, or video conferences.
- Advantages: Immediate feedback, personal connection, and easier to convey emotions.
- Disadvantages: Lack of permanent record, chance of misinterpretation due to unclear speech.
b. Written Communication
This form includes emails, reports, memos, letters, and official documents. Written communication is widely used in business for documentation and formal interactions.
- Advantages: Creates a permanent record, can be edited and revised before sending, used for formal or legal purposes.
- Disadvantages: Lacks immediacy, tone may be misunderstood without context.
c. Non-verbal Communication
This refers to communication without words, including body language, gestures, facial expressions, posture, and eye contact.
- Importance in Professional Communication: Non-verbal cues can enhance or contradict what is being said verbally. It’s crucial to be aware of non-verbal signals in face-to-face interactions, especially in interviews, presentations, and meetings.
5. Principles of Effective Professional Communication
- Know Your Audience: Tailor your message based on the needs, interests, and understanding of the people you’re communicating with.
- Active Listening: Pay attention, ask clarifying questions, and show that you’re engaged in the conversation.
- Feedback: Encourage and provide feedback to ensure the message has been understood correctly.
- Tone and Language: Use an appropriate tone (formal, polite) and clear language suited to the professional environment.
6. Barriers to Communication
- Physical Barriers: Distance or poor infrastructure (e.g., bad internet connection in virtual meetings).
- Psychological Barriers: Prejudices, emotions, or anxiety that affect understanding.
- Language Barriers: Differences in language or jargon that can create confusion.
- Cultural Barriers: Misunderstandings arising from cultural differences in communication styles or body language.
7. Listening Skills in Professional Communication
Active Listening is a key skill in professional communication. It involves:
- Paying full attention to the speaker.
- Not interrupting.
- Summarizing or paraphrasing the speaker’s points to ensure understanding.
- Providing appropriate feedback.
8. Professional Written Communication
Emails, reports, and proposals are common types of written communication in a professional setting. Here are some tips for effective written communication:
- Structure: Use a clear structure with an introduction, body, and conclusion.
- Tone: Keep it formal and polite. Avoid slang or overly casual language.
- Proofread: Always check for grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and clarity before sending.
9. Technology and Communication
In the digital age, technology plays a significant role in professional communication:
- Email: The most commonly used tool for professional communication. Emails should be formal, concise, and to the point.
- Video Conferencing: Tools like Zoom, Google Meet, and Microsoft Teams have become essential for virtual meetings and interviews.
- Social Media and Networking: LinkedIn and other platforms help professionals network, share ideas, and communicate with a wider audience.
10. Presentation Skills
Presenting information clearly and engagingly is a crucial part of professional communication. Key aspects of good presentation skills include:
- Preparation: Know your material and the audience you’re addressing.
- Visual Aids: Use slides, charts, or other visuals to support your points.
- Confidence and Body Language: Stand tall, maintain eye contact, and use appropriate gestures to emphasize points.
- Clarity and Pacing: Speak clearly and at a measured pace to ensure the audience can follow.
11. Ethics in Professional Communication
Ethical communication is vital for maintaining integrity and professionalism in the workplace. This includes:
- Honesty: Always present information truthfully.
- Confidentiality: Respect privacy and do not share sensitive information without permission.
- Respect: Show respect to all individuals, regardless of their position or background.
12. Cross-Cultural Communication
In global business environments, cross-cultural communication is crucial. Professionals must be aware of cultural differences in communication styles, gestures, and etiquette to avoid misunderstandings and build positive relationships.
13. Group Communication and Teamwork
In professional settings, communication often happens within teams. Effective group communication involves:
- Collaboration: Sharing ideas and working together to achieve common goals.
- Leadership: A leader’s ability to communicate clearly and motivate the team is essential for success.
- Conflict Resolution: Open communication can help resolve misunderstandings or conflicts that may arise within a team.
14. Conclusion
Professional communication is a skill that is crucial for success in any career, especially in the technical and business fields. Mastering both verbal and written communication, understanding non-verbal cues, and adapting to new technological tools are essential to becoming an effective communicator.
These notes cover the foundational aspects of professional communication and should help you grasp the essential skills needed for your BTech course.
Here are detailed notes on the topics mentioned in the academic syllabus related to Professional Communication, organized in the order mentioned in the syllabus provided:
1. Importance of Communication
Communication is essential in both personal and professional life as it:
- Facilitates Understanding: Clear communication ensures the accurate exchange of ideas, helping individuals understand each other better.
- Builds Relationships: Effective communication strengthens interpersonal and professional relationships.
- Improves Decision-Making: With accurate information and clarity, better decisions can be made.
- Promotes Teamwork: Helps in coordinating efforts, reducing misunderstandings, and enhancing collaboration.
- Career Advancement: Good communication skills help individuals stand out and achieve professional success.
2. Importance of Communication in English
English is often regarded as the global language of business, and its importance in professional communication includes:
- Global Reach: English is widely used in international business, allowing for smoother communication across borders.
- Professional Documentation: Most formal documents, reports, and research papers are written in English.
- Employment Opportunities: Proficiency in English opens doors to better job prospects in multinational companies.
- Collaboration: Helps in collaborating with global teams, as it is the most common second language.
3. Concept of Effective Communication
Effective Communication occurs when the message is clearly sent, received, and understood as intended. The key elements of effective communication include:
- Clarity: The message should be easy to understand.
- Purpose: The communication must have a specific goal or objective.
- Feedback: It’s important to get feedback to ensure the message is understood.
- Adaptability: Adapting the message according to the audience ensures better comprehension.
- Listening: Active listening ensures that the receiver understands the message properly.
4. Assertive Communication
Assertive Communication is the ability to express one’s thoughts, opinions, and needs in a direct, honest, and respectful manner.
- Characteristics of Assertive Communication:
- Confidence without being aggressive.
- Clear and respectful expression of thoughts.
- Maintaining eye contact and positive body language.
- Benefits:
- Encourages open dialogue.
- Prevents misunderstandings and conflicts.
- Builds mutual respect in professional relationships.
5. Communication and Self-Concept
Self-concept is an individual’s perception of themselves, which impacts how they communicate with others. It includes:
- Self-awareness: Understanding one’s strengths and weaknesses influences how confidently a person communicates.
- Self-esteem: Higher self-esteem usually results in more confident and effective communication.
- Impact on Communication: Positive self-concept leads to open and assertive communication, while negative self-concept can result in passive or defensive communication styles.
6. Role of Emotions in Communication
Emotions significantly impact the way we communicate. The role of emotions in communication includes:
- Influence on Tone: Emotions can affect the tone and mood of communication (e.g., anger may lead to an aggressive tone).
- Non-verbal Cues: Emotions are often expressed through body language, facial expressions, and gestures.
- Impact on Clarity: Strong emotions like anxiety or frustration can cause miscommunication or lead to misunderstandings.
- Emotional Intelligence: Being aware of and managing emotions helps in maintaining professionalism and empathy during communication.
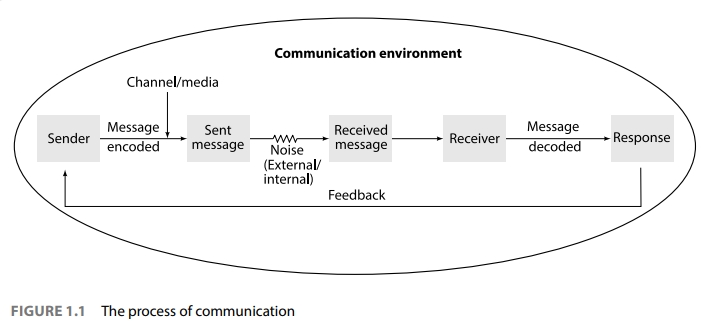
7. Process of Communication
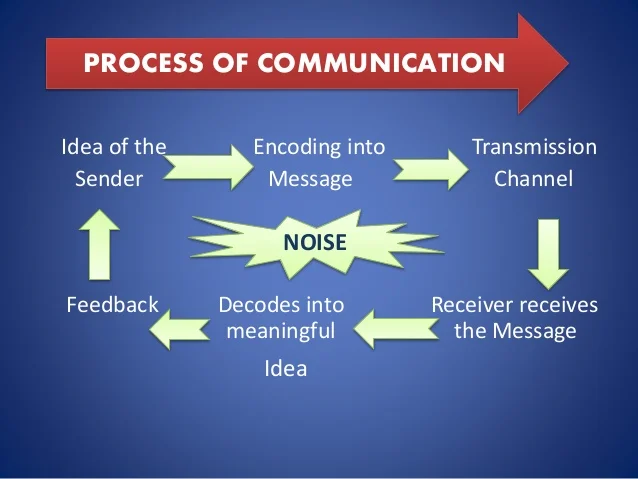
The process of communication involves several key steps:
- Sender: The person who initiates the message.
- Encoding: Converting the idea or information into a message.
- Message: The content being communicated.
- Channel: The medium (verbal, written, non-verbal) through which the message is sent.
- Receiver: The person who receives the message.
- Decoding: Interpreting and making sense of the message.
- Feedback: The response from the receiver, indicating if the message was understood.
8. Knowing the Purpose and Audience
Effective communication requires understanding:
- Purpose: Knowing the goal of the communication (e.g., informing, persuading, instructing) helps in structuring the message clearly.
- Audience: Tailoring communication based on the audience’s background, level of understanding, and expectations ensures relevance and effectiveness.
9. Types of Communication
a. Formal Communication
- Definition: Official communication that follows a set structure or protocol within an organization.
- Examples: Emails, reports, memos, and meetings.
b. Informal Communication
- Definition: Casual, unofficial communication between colleagues or peers.
- Examples: Conversations during breaks, casual emails, or instant messages.
c. Verbal Communication
- Definition: Communication that uses spoken words.
- Examples: Meetings, presentations, phone calls.
d. Non-verbal Communication
- Definition: Communication through body language, facial expressions, gestures, and eye contact.
- Importance: Non-verbal cues can support or contradict what is being said verbally.
e. Interpersonal Communication
- Definition: Direct communication between two or more individuals.
- Importance: Key to building relationships and working collaboratively in teams.
f. Intrapersonal Communication
- Definition: Communication with oneself, including self-reflection and inner dialogue.
- Importance: Affects self-awareness and decision-making.
g. Cross-Cultural Communication
- Definition: Communication between people from different cultures or backgrounds.
- Challenges: Differences in language, non-verbal cues, and communication styles.
- Importance: Essential in global business to avoid misunderstandings and foster collaboration.
10. Organisational Communication
Organizational Communication refers to the ways in which information flows within an organization.
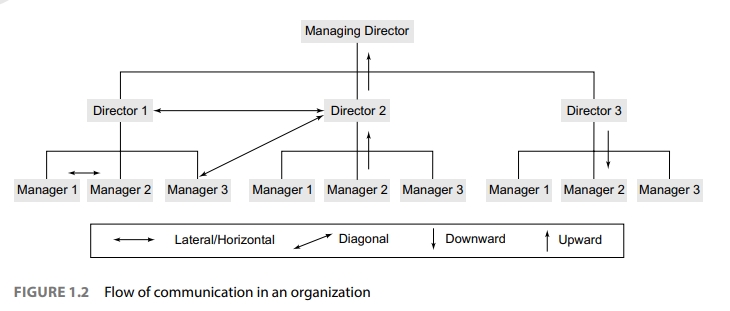
a. Formal Channels of Communication
- Upward Communication:
- Information flows from lower levels of the hierarchy to higher levels (e.g., employee to manager).
- Importance: Helps management understand employee feedback and issues.
- Downward Communication:
- Information flows from higher levels to lower levels (e.g., manager to employee).
- Importance: Ensures instructions, policies, and expectations are communicated clearly.
- Horizontal Communication:
- Communication between individuals or teams at the same level (e.g., peer-to-peer).
- Importance: Promotes coordination and collaboration across departments.
- Diagonal Communication:
- Cross-departmental communication between individuals at different levels.
- Importance: Encourages collaboration between different functions or divisions.
b. Informal Channel of Communication: Grapevine
- Definition: Unofficial, casual communication that occurs in organizations.
- Characteristics: Often based on rumors or informal conversations.
- Advantages: Can spread information quickly and encourage social bonding.
- Disadvantages: Information may be inaccurate or lead to misunderstandings.
11. Barriers to Communication
Barriers to communication hinder the effective exchange of information. Some common barriers include:
- Physical Barriers: Poor infrastructure, distance, or noisy environments.
- Psychological Barriers: Emotions, stress, or preconceived notions that affect understanding.
- Language Barriers: Differences in language or jargon.
- Cultural Barriers: Differences in values, beliefs, or customs that affect interpretation.
- Perceptual Barriers: Differences in how individuals perceive and interpret information.
12. Tips for Effective Communication
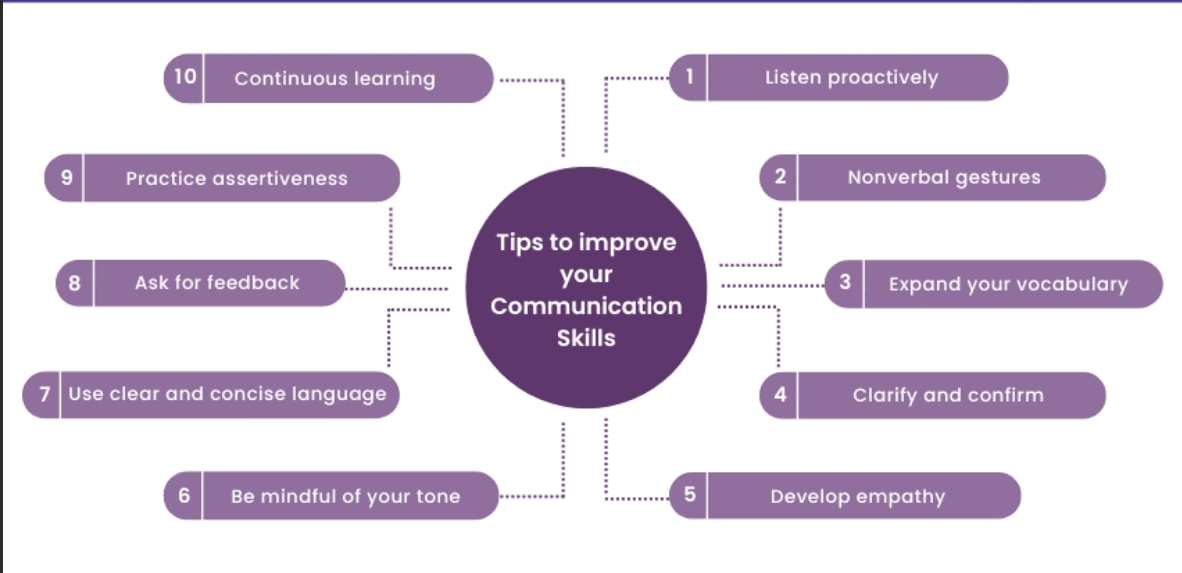
To communicate effectively, consider the following tips:
- Be Clear and Concise: Avoid unnecessary details and focus on the core message.
- Active Listening: Pay attention to the speaker, ask clarifying questions, and provide feedback.
- Maintain Appropriate Body Language: Use non-verbal cues that align with your message (e.g., eye contact, gestures).
- Adapt to Your Audience: Tailor your message based on the audience’s background and expectations.
- Provide and Seek Feedback: Encourage feedback to ensure the message is understood and to improve future communication.
- Stay Open and Empathetic: Be receptive to others’ viewpoints and show understanding in your responses.

These notes comprehensively cover the topics related to Professional Communication for a BTech 1st year course. Let me know if you need further elaboration or clarification on any of these points!